The Science Behind Heat Resistance in Hot Paper Cups Explained

Hot paper cups can handle heat because of special materials and smart designs. Many people have felt a hot drink burn their hand through a thin cup. This usually happens with single-wall disposable cups, especially with very hot drinks. In busy places like takeout spots or office break rooms, people use hot beverage cups to drink coffee or tea safely. Double-wall and ripple-wall hot paper cups help stop heat from moving to your hand. This makes it safer to hold hot drinks without hurting yourself. Knowing how these cups work helps keep daily life safe and comfortable.
Key Takeaways
Hot paper cups use thick paperboard and special coatings. These help keep drinks hot. They also protect your hands from burns. Double-wall and ripple-wall designs trap air between layers. This slows heat transfer. It keeps the outside of the cup cooler. Coatings like polyethylene and PLA block water and heat. This stops leaks and keeps the cup strong with hot drinks. Smart cup designs mean you do not need extra sleeves. This makes hot drinks safer and more comfortable to hold. Most hot paper cups are hard to recycle because of their coatings. Look for food-safe labels and think about the environment.
How Hot Paper Cups Resist Heat
Key Principles
Hot paper cups stay cool to touch because of smart design and materials. Many science ideas work together to keep your hands safe.
The cup is made from paperboard. This gives it strength and shape. Inside, there is a thin layer called a coating. It is usually made from polyethylene or PLA. This coating keeps water out and slows heat from moving.
If the coating is thicker or better, it works even more. It helps keep your hand comfortable when you hold the cup.
Some cups have double walls or special handles. These make air gaps or let you hold the cup without touching the hottest part. Air does not let heat move fast, so the outside stays cooler.
The cup’s design stops heat from moving by conduction and convection. This means less heat goes from the drink to your hand.
Companies test these cups with strict rules. This makes sure they work well and are safe for hot drinks.
Note: Hot paper cups use both special materials and smart building. This keeps drinks hot but protects your hands from burns.
Why Paper Alone Isn’t Enough
Paper alone cannot stop heat from moving through. The fibers in paper let heat and water pass easily. If you pour a hot drink in a plain paper cup, heat moves through fast. The cup gets too hot to hold. The paper can get weak or even leak.
To fix this, companies add coatings and use thicker paperboard. Double-walled cups have two layers with air between them. The air acts as insulation. This keeps the outside cooler and the drink hot longer. Some cups use paperboard as thick as 220-300 grams per square meter. This makes the cup stronger and better at stopping heat. The coating, like polyethylene or PLA, keeps liquid out and blocks heat.
Physical laws, like Fourier’s law of heat conduction, explain how heat moves. Thicker paper and better insulation mean less heat gets out. Double-wall designs use these ideas to keep cups safe for hot drinks.
Table: How Different Features Improve Heat Resistance
Feature | How It Helps |
|---|---|
Thicker Paperboard | Slows down heat transfer |
Polyethylene/PLA Coating | Blocks moisture and heat |
Double-Wall Design | Adds an insulating air gap |
Quality Testing | Ensures safety and performance |
Hot paper cups use these features to work better than plain paper cups. This smart design lets people enjoy hot drinks safely and comfortably.
Materials in Hot Paper Cups

Paperboard Types
Hot paper cups are made with food-safe paperboard. This paperboard is strong and safe for drinks. Sometimes, companies add recycled fibers or cardboard. This makes the cup tougher and better at keeping heat in. Double-wall and ripple-wall cups have extra layers. These layers trap air inside the cup. Air helps keep the outside of the cup cooler. This design keeps drinks hot and protects your hands from burns.
Construction Details | Thermal Properties and Use Case | |
|---|---|---|
Single Wall Paper Cups | Single layer of paperboard | Lightweight, affordable, basic insulation for hot and cold drinks |
Double Wall Paper Cups | Two layers of paperboard with an air gap | Superior insulation and heat retention; keeps beverage warm longer; exterior remains cooler |
Ripple Wall Paper Cups | Additional corrugated paper layer creating ripple effect | Improved insulation and grip; commonly used in cafes/restaurants |
Insulated Handle Paper Cups | Incorporate insulating materials like foam or air pockets | Enhanced heat retention; suitable for prolonged temperature maintenance |
The thickness and finish of the paperboard matter too. Matt finishes have tiny air pockets. These pockets help keep heat inside and make the cup cooler to touch. Glossy finishes do not trap as much air. So, glossy cups feel warmer on the outside.
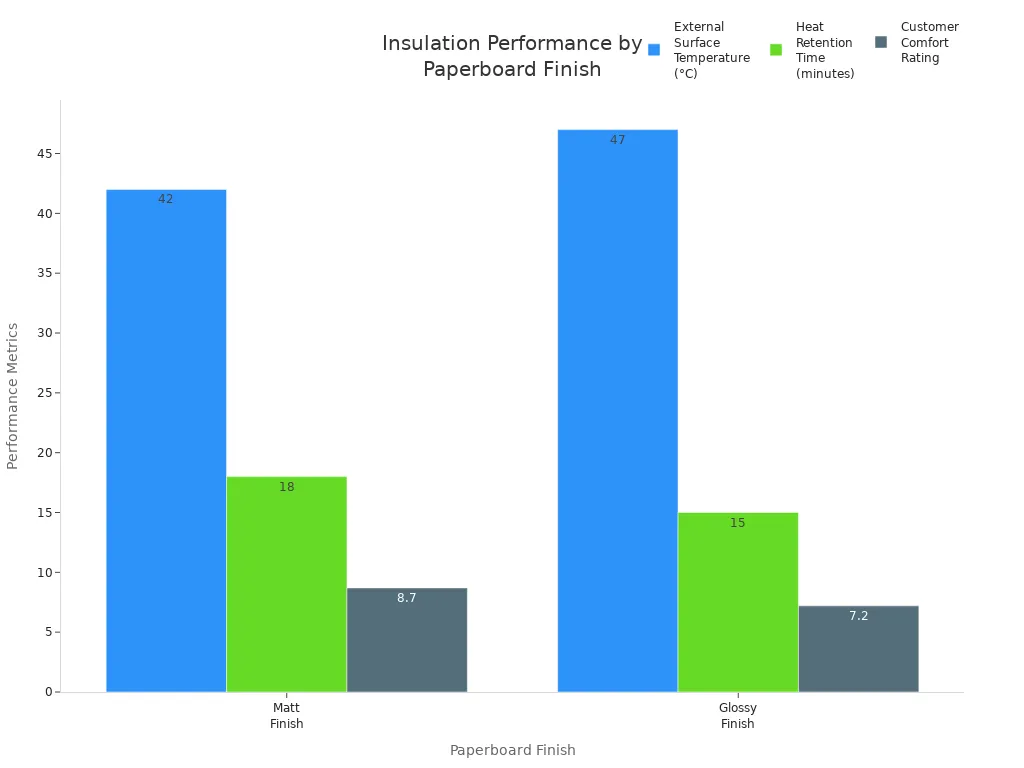
Studies show that thicker paperboard can move heat faster. This means it does not always keep drinks hot as well. To make the best cup, companies balance thickness and finish. This helps keep drinks hot and hands safe.
Coatings and Liners
All hot paper cups need a special coating. This coating stops leaks and keeps water out. Most cups use polyethylene or other special coatings. These coatings are very thin, about 20 to 50 microns thick. They block both water and heat. Polyethylene coatings can handle drinks up to 90°C.
Some coatings are hydrophobic, which means they push water away. This helps the cup stay strong. Some cups use coatings that are better for the environment. Additives and adhesives help seal the cup tight. They also help the cup keep its shape when holding hot drinks. Hydrophobic coatings and barrier layers work together. They stop leaks and keep the cup strong. This makes hot paper cups safe for everyday use.
Note: Barrier coatings, water resistance, and thermal stability help hot paper cups hold hot drinks safely without leaking or getting weak.
Heat Resistance Mechanisms
Thermal Conductivity
Hot paper cups slow down heat moving through them. This is because of a property called thermal conductivity. If something has low thermal conductivity, heat does not pass through it fast. This keeps the outside of the cup cooler, even if the drink is very hot.
Plastic foams, like polystyrene foam, have very low thermal conductivity. Their numbers are between 0.03 and 0.05 W/m·K. This means they are great at stopping heat. Solid plastics, such as polypropylene, let heat move faster. Their number is about 0.22 W/m·K. Paper cups are in the middle. They let more heat through than foam, but less than solid plastic. So, hot paper cups give medium heat resistance. They do not keep heat in as well as foam cups, but they are better than many plastic cups.
Thermal effusivity is also important. It tells how fast a material gives heat to things around it. If something has low thermal effusivity, it gets warm on the surface but does not send much heat to your hand. Hot paper cups use materials with low thermal effusivity. When you hold a hot paper cup, it feels warm but does not burn you. This makes the cup safer and more comfortable.
Tip: Low thermal conductivity and low thermal effusivity help keep the cup safe to hold. They work together to stop your hand from getting too hot.
Insulation and Air Pockets
The way hot paper cups are built helps stop heat too. Many cups have two walls with a small air pocket between them. The air pocket acts as a barrier. Air does not let heat move quickly, so it slows down heat from the drink to the outside.
Double-wall cups use this air gap to make heat resistance better. The air layer keeps drinks warm longer and the outside cooler. This design also makes the cup stronger, so it does not break or leak easily. Many coffee cups use this idea. The air pocket means you do not need an extra sleeve, so the cup is easier and safer to use.
Double-wall cups have two layers and an air gap. This stops heat from reaching the outside fast. The outside stays much cooler than single-wall cups.
Single-wall cups do not block heat well. Heat moves out quickly, so you often need a sleeve.
Double-wall cups keep drinks hot and hands safe. They also make serving drinks faster and use fewer sleeves.
Better insulation in double-wall cups keeps the outside cooler. This makes them safer and more comfortable for people.
Low thermal conductivity, low thermal effusivity, and smart designs like air pockets all help hot paper cups resist heat. These things work together to keep drinks hot and protect your hands.
Design Innovations

Double-Wall Cups
Double-wall cups have made drinking hot drinks easier. These cups have two layers of paperboard with air between them. The air gap works as insulation. This helps keep drinks warm for a longer time. You can hold these cups without burning your hand. Double-wall cups do not need extra sleeves.
The table below shows how single-wall and double-wall cups are different:
Criteria | Single-wall Cups | Double-wall Cups |
|---|---|---|
Insulation | Not much insulation; heat goes right to the outside, so you often need a sleeve | Better insulation from two layers; keeps drinks warmer and is easy to hold without a sleeve |
Comfort | Usually needs a sleeve for hot drinks | Easy to hold, even with hot drinks |
Durability | Not as strong | Stronger and does not bend easily |
Cost | Cheaper | Costs more but saves money on sleeves |
Best Use Case | Cold drinks or hot drinks you drink fast | Hot drinks you want to stay warm longer |
Double-wall cups cost more at first. But they save money because you do not need sleeves. They also keep drinks warm and are more comfortable. Many coffee shops use double-wall cups for takeaway drinks.
Structural Features
Cup makers add special features to help with heat resistance. Double-wall or triple-wall cups have air pockets or more paper layers. These stop heat from moving out fast. Ribbed textures on the cup give more insulation. The ribbing also makes the cup easier to hold and helps stop burns.
Double-wall kraft paper cups insulate better than single-layer cups.
Ribbed textures help keep heat in and make holding the cup nicer.
Stronger bottoms and sides make the cup last longer.
Heat-resistant coatings inside slow down heat leaving the cup.
Embossing adds insulation and makes the cup tougher.
Some double-wall cups keep drinks hot up to four hours longer than single-wall cups. These designs make hot paper cups safer and better for hot drinks. They help people avoid burns and enjoy drinks at the right temperature.
Safety and Effectiveness
Temperature Limits
Hot paper cups need to handle very hot drinks. Most cups use food-grade paperboard with a special coating. This coating is usually made from polyethylene or PLA. It acts as a barrier to heat and liquid. These materials let the cup hold drinks up to 190°F (88°C). The cup does not leak or lose its shape at this temperature. When you pour a hot drink in, the coating stops the liquid from soaking into the paper. The cup stays strong and does not get soggy. Double-wall and ripple-wall cups give extra protection. They help the cup resist heat and keep the outside cooler. Food safety rules, like those from the FDA, make sure these cups are safe. They do not release harmful chemicals when used with hot drinks.
Tip: Always look for a food-safe label on your cup. This shows the cup meets safety standards for hot drinks.
Durability and Leaks
A hot paper cup must be strong and not leak. The cup’s strength depends on the paper weight and coating quality. Heavier paper makes thicker walls. This helps the cup not bend or break with hot drinks. The coating keeps the cup from leaking, even after many uses. Double-wall and ripple-wall cups protect better and last longer. They also lower the chance of leaks or the cup changing shape. Makers test these cups to meet safety rules. Good cups do not leak or fall apart, even after holding hot drinks many times. Bad coatings can fail at high heat. This can cause leaks or let chemicals mix with the drink. Trusted brands use strong coatings and follow food safety rules. This keeps your drink safe and stops spills.
Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
Heavy Paperboard | Stronger walls, less bending |
Quality Coating | Prevents leaks, resists high heat |
Double/Ripple Walls | Extra durability, better heat resistance |
Food Safety Standards | No harmful chemicals, safe for hot use |
Environmental Impact
Recycling and Composting
Hot paper cups are hard to recycle or compost. Most cups have a plastic or wax coating to stop leaks. These coatings stick tightly to the paper. This makes it tough for recycling centers to pull the materials apart. Many places do not take these cups. The plastic or wax can break recycling machines or ruin other paper.
Plastic coatings like polyethylene make paper break down slower.
Wax coatings come from petroleum and do not compost well. They can leave behind bad chemicals.
The plastic lining can mix with other paper and make sorting hard.
Composting needs the plastic or wax removed to keep compost safe.
Some cups use compostable liners like PLA, but these are rare.
Most recycling centers cannot handle these cups because of the coatings and melting points.
Note: Special recycling or composting systems are needed for coated hot paper cups. Without these, most cups go to landfills.
Material Safety
People worry about chemicals in hot paper cups. Some coatings and additives can move into hot drinks. These chemicals might be risky if people drink them often.
Chemical/Additive Type | Description and Source | Safety Concern for Consumers |
|---|---|---|
Phthalate compounds | Plasticizers used to make plastics flexible | May leach into hot drinks, possible health risks |
Antioxidant additives | Used to slow down plastic breakdown | Can migrate into beverages, raising safety concerns |
Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAs) | Used for waterproofing and oil resistance | Known to leach into liquids, linked to toxicity |
Heavy metals | Found in some plastic liners | Can transfer into drinks, long-term health hazards |
Microplastics | Released from plastic liners when exposed to hot water | Ingested through drinks, health effects not fully known |
Groups like the FDA and the European Union check cup safety. They test if chemicals move from the cup into drinks. These groups set strict rules for what chemicals can be used. They also want clear labels and regular checks to keep people safe.
Tip: Always pick cups labeled food-safe and approved by trusted groups. This helps lower health risks from chemicals in hot paper cups.
Hot paper cups have special coatings and smart designs. These help keep hot drinks safe to drink. The table below shows how each coating works for heat, safety, and the environment:
Coating Material | Heat Resistance | Environmental Impact | Safety and Performance Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Polyethylene (PE) | Up to 100°C | Recyclable with limits | Stable, affordable, widely used |
Polylactic Acid (PLA) | 60°C–85°C | Compostable, plant-based | Eco-friendly, less for boiling drinks |
Water-Based Coating | Up to 90°C | Biodegradable, recyclable | New, growing in use |
Hot drinks stay warm but do not burn your hands.
Food safety rules make sure cups do not have bad chemicals.
Material science helps cups be safer and better for nature.
Material science helps make things we use every day. It lets people drink hot drinks safely and helps the planet too.
FAQ
What makes hot paper cups safe for hot drinks?
Hot paper cups use thick paperboard and special coatings. These materials stop leaks and slow heat transfer. The design keeps hands safe from burns. Food safety rules check that the cups do not release harmful chemicals.
Can you recycle hot paper cups?
Most recycling centers cannot process hot paper cups. The plastic or wax coating sticks to the paperboard. This makes separation hard. Some cities have special recycling programs for these cups.
Why do some cups have a ripple or double wall?
Ripple and double-wall cups trap air between layers. Air acts as insulation. This design keeps the outside cooler and the drink hot longer. People can hold these cups without burning their hands.
Are all coatings on hot paper cups safe?
Most coatings, like polyethylene and PLA, meet food safety standards. Regulatory groups test these materials. They make sure coatings do not release unsafe chemicals into drinks.
How long can a hot paper cup keep a drink warm?
A double-wall or ripple-wall cup can keep a drink warm for up to 30–60 minutes. The insulation slows heat loss. Single-wall cups lose heat faster and may need a sleeve for comfort.